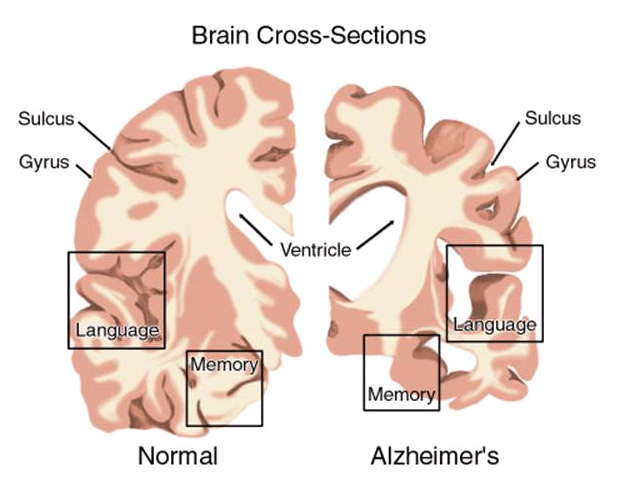
 Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by loss of recent memory, confusion, disorientation and sometimes a change in personality. Patients suffer from progressive degeneration and loss of brain cells and acetylcholine, the chemical messenger needed for memory. Insulin signaling decreases due to insulin resistance. Free iron and abnormal proteins accumulate in the brain in the form of plaques and tangles.
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by loss of recent memory, confusion, disorientation and sometimes a change in personality. Patients suffer from progressive degeneration and loss of brain cells and acetylcholine, the chemical messenger needed for memory. Insulin signaling decreases due to insulin resistance. Free iron and abnormal proteins accumulate in the brain in the form of plaques and tangles.
Other causes of memory loss include deficiencies of thyroid hormone or vitamin B12; also small strokes can affect memory and cognition. These causes of memory loss can be detected with blood tests or a brain scan such as a CT or MRI.
Individuals with significant memory loss should get a thorough neurological exam to rule out other potential causes of dementia.


